How are harmonics created and what are the benefits of harnessing harmonics?
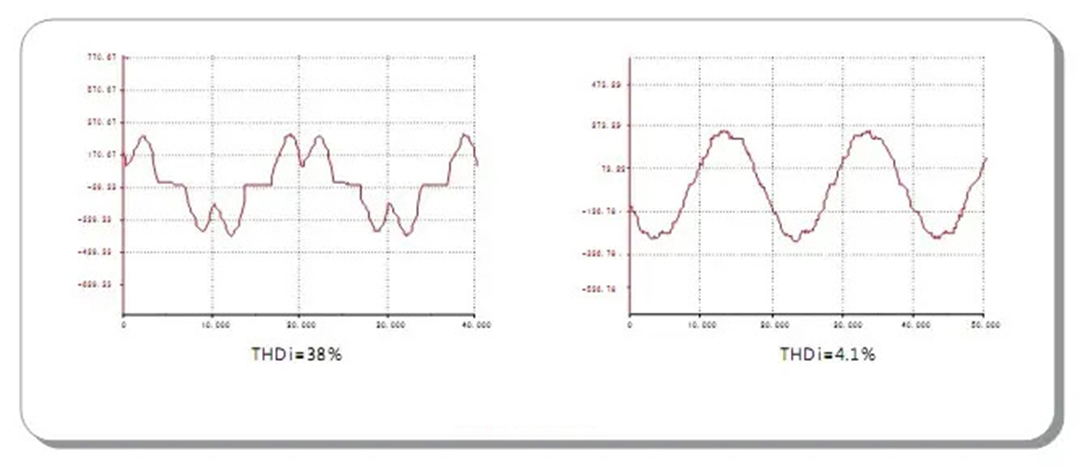
Harmonic refers to the electric quantity whose frequency is an integer multiple of the fundamental wave contained in the current. It generally refers to the Fourier series decomposition of periodic non-sinusoidal electric quantity, except for the electric quantity of fundamental frequency, the amount of electricity generated by the rest of the current greater than the fundamental frequency is called harmonics. the harmonic order is the ratio of the harmonic frequency to the fundamental frequency (n=fn/f1).
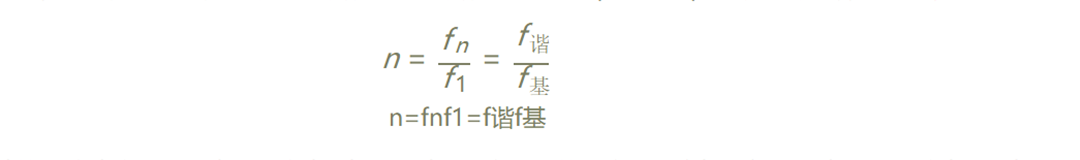
There are a large number of nonlinear loads in the power system: large-scale power electronic application devices (energy-saving devices, frequency conversion equipment, etc.), high-power electric drive equipment, DC output devices, electrochemical industrial equipment (rectification of chemical and metallurgical enterprises), electrified railways, Steelmaking electric arc furnace (AC, DC), rolling mill, hoist, calcium carbide furnace, induction heating furnace and other nonlinear loads. In addition, there are many fast-changing impact loads, such as large motors and motor groups, high-speed elevators in high-rise buildings, electric flying cars in large amusement parks, electric welding machines in automobile manufacturers, high-speed railways, high-speed maglev trains and subways, cranes in ports and other fast-changing loads.

While realizing power control and processing, new power equipment with nonlinear and impulsive loads inevitably generates non-sinusoidal waveform current, injects harmonic current into the power grid, which severely distorts the voltage waveform at the common connection point (PCC). Load fluctuation and impulsive characteristics cause voltage fluctuation, instantaneous pulse, and other power quality disturbances. With the extensive use of nonlinear and impact loads, power quality problems will become more prominent, and the impact and harm to grid operation and sensitive electrical equipment will become more obvious. The possibility of power accidents will gradually be caused by unqualified power quality.
Benefits of harmonic control:
Direct connection benefits: 1. Protect capacitors from interference, 2. Reduce loss, 3. Reduce heating of lines and buses, 4. Protect electric equipment.
Indirect benefits: improve the power quality of the system, reduce the capacity burden of the distribution system, and protect the safe and stable operation of electrical equipment.
Social benefits: eliminate harmonics from the source of each low-voltage harmonic source, prevent harmonic current from flowing into the upper power grid, and contribute to the construction of a power grid with perfect power quality.