Effect of harmonics on power transformers?
Background Introduction
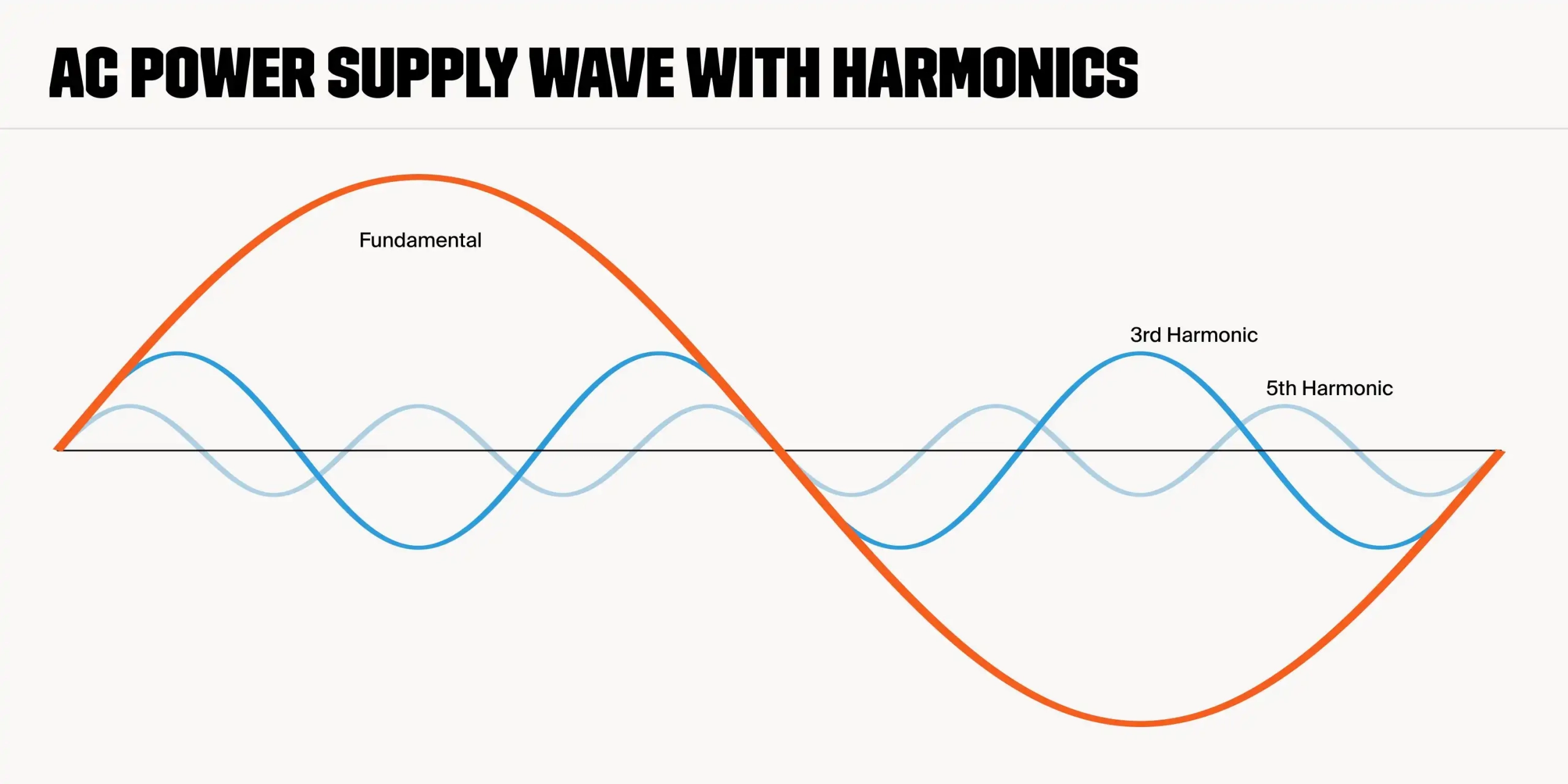
Transformers are regarded as critical components in power systems. In single-phase transformers, the measurement of the iron and copper losses is significant, specifically for transformers that feed nonlinear loads. Power losses due to increased harmonic distortions and abnormal increases in the transformer temperature can be attributed to core stray magnetic losses, losses in the windings, and eddy currents. Thus, harmonics can have a detrimental effect on the power factor of capacitors when fitted and hence, resonance must be avoided in the supply inductance. Moreover, in the presence of harmonics, there is an approximate increase in the eddy current with the square of the current and as such, eddy current presents the most concern among the sources of current losses in transformers. This necessitates the determination of the harmonic spectrum of load currents prior to the estimation of excess losses.
In the power systems, the use of nonlinear loads can often lead to reduction in the service life of a transformer because of the possible influence of increased heat losses. Therefore, certain conditions ought to be met before analyzing the performance of a transformer, such as a knowledge of the load mix, the total harmonic distortion (THD), and the details of the content of the load current harmonics. Two factors that contribute to the additional heating observed in a transformer, these are the design principles of the transformer and the load current harmonics.
How to reduce harmonics
In general, the effect of harmonics can be mitigated by selecting equipment with low THD currents, thereby reducing the effective THD voltage. However, in the case that the use of equipment with low THD current is prohibitive, alternative options exists such as the addition of line chokes or isolation transformers to reduce the harmonic currents. Moreover, current distortions, which have a pronounced effect on the voltage waveform, can be reduced by using a tuned capacitor. In addition, the system load distribution can be redesigned such that the total system impedance is reduced. Several solutions have been proposed for reducing the effects of harmonics, and are as follows
1.Reduction of current harmonics
Through the addition of line chokes to the harmonics producing equipment.
Through the addition of an isolation transformer to the harmonics producing equipment.
Through the use of a 12- pulse or 18-pulse rectifying circuit instead of 6-pulse rectifying circuit.
2.Reduction of voltage harmonics
Through the addition of a tuned capacitor bank to the source of current harmonics.
Through optimization of transformer size and impedance.
3.Through the use of cost-effective and energy-efficient phase-shifting transformers, which are highly reliable passive devices that can control harmonics regardless of the load level served
Effect of harmonics on transformer losses In general, transformers are designed to have minimum losses in both sinusoidal currents and rated voltage. However, the load current is no longer sinusoidal because of the increase in the number of nonlinear loads. Thus, the presence of the nonsinusoidal currents leads to in extra losses and increase in transformer temperature. There are several ways of estimating harmonic load content, such as the use of the crest-factor, percent of THD, and the K-Factor, which can be used to determine the extra heat generated by nonsinusoidal loads.