Benefits of reactive power compensation
Reactive power is the electrical power used for the exchange of electric field and magnetic field in the circuit and used to establish and maintain the magnetic field in electrical equipment. It does not work externally but is converted into other forms of energy. All electrical equipment with electromagnetic coils will consume reactive power to establish a magnetic field. Reactive power does not work, but to ensure the conduction of active power, it must first meet the reactive power of the grid.
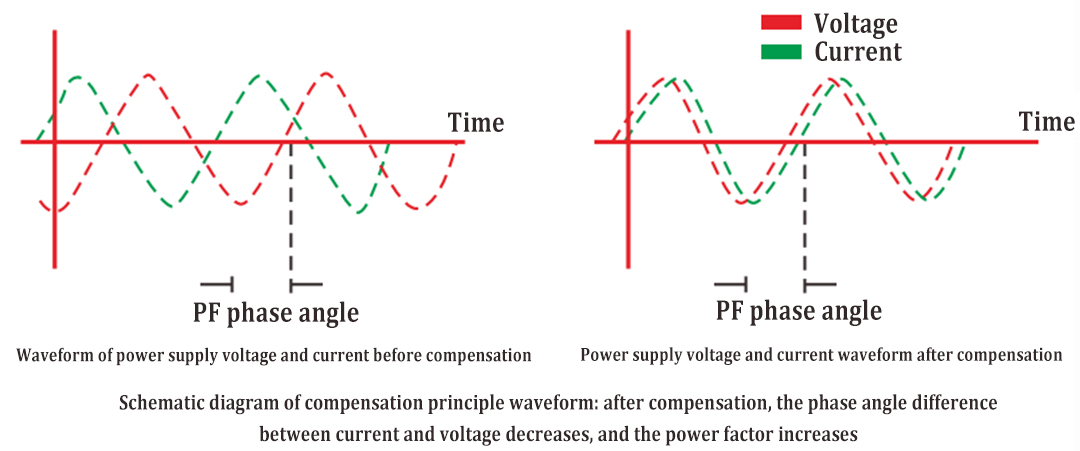
Under normal conditions, electrical equipment not only needs to obtain active power from the power supply, but also needs to obtain reactive power from the power supply. If the reactive power in the power grid is in short supply, the electrical equipment will not have enough reactive power to establish a normal electromagnetic field, and this electrical equipment will not be able to work at rated conditions, and the terminal voltage of the electrical equipment will drop, thus affecting the normal operation of the electrical equipment. However, the reactive power supplied from the generator and high-voltage transmission line can not meet the demand of the load. Therefore, some reactive compensation devices should be set in the power grid to supplement the reactive power to ensure the user’s demand for reactive power, so that the electrical equipment can work at the rated voltage. Reactive compensation refers to the device with a capacitive power load and inductive power load connected in the same circuit, and the energy is exchanged between the two loads. In this way, the reactive power required by the inductive load can be compensated by the reactive power output by the capacitive load.
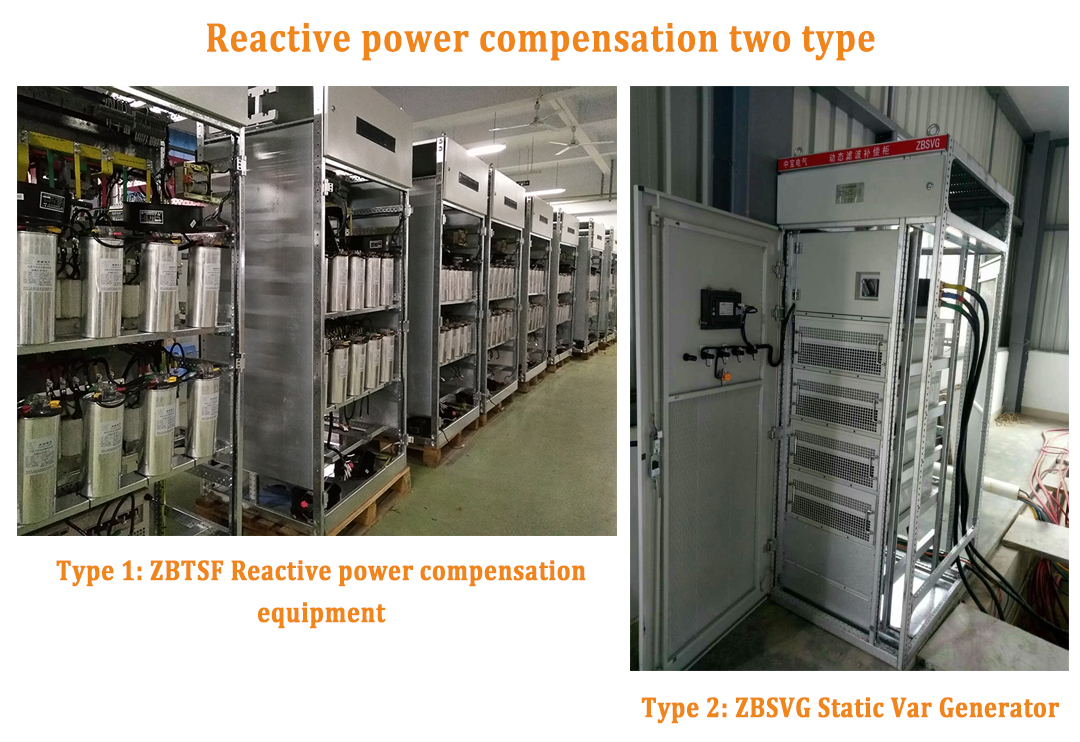
Reactive power compensation two type: TSF Reactive compensation equipment, SVG Static Var Generator.
Reactive compensation governance benefits:
- Adopting reactive power compensation technology to improve the power factor of low-voltage power grid and electrical equipment is an important measure for power saving
- Reactive power compensation is to provide necessary reactive power with the help of reactive power compensation equipment to improve the power factor of the system, reduce energy consumption, improve the voltage quality of the power grid, and stabilize equipment operation
- Reduce power loss. Generally, the power wiring of the factory is subject to power loss according to different lines and load conditions; About 20% – 30%. After using capacitors to improve the power factor, the total electric wave will be reduced, which can reduce the power loss of the supply current and the power terminal.
- Improve the power supply quality, improve the power factor, reduce the total load current and voltage drop, and install capacitors on the secondary side of the transformer to improve the power factor and increase the secondary side voltage.
- The service life of the equipment is extended. After the power factor is improved, the total current of the line is reduced, so that the capacity load of the transformer, switch and other machinery equipment and the line that are close to saturation is reduced. Therefore, the temperature rise can be reduced and the service life can be increased (the service life can be extended by one time for every 10 ℃ temperature reduction).
- Finally, it can meet the monitoring requirements of power system for reactive power compensation, and eliminate the fines caused by low power factor.
- Reactive power compensation can improve power quality, reduce power consumption, tap the potential of power generation and supply equipment, and reduce the user’s electricity cost. It is an energy-saving measure with less investment and quick results.
- The impact of reactive power compensation technology on the low-voltage distribution network of HEDI and the economic and social benefits brought by improving the power factor, determine the compensation capacity of reactive power, ensure that the compensation technology is economic, reasonable, safe and reliable, and achieve the purpose of saving electric energy.